

The conveyed information must be enough for the execution person. Orifice meter taps orientation (it depends upon the pipe direction and fluid typeīOM section is a very important section, as it affects the cost of the project.After establishing a 3-D model in PDMS, SP3D, or any other software, Piping designers have to communicate the same information to the person who is executing that piping job either in the yard for fabrication or in the field for Erection/Construction.Minimum gap requirement between the welds.Field weld and Workshop weld Identification.Structural penetration (if the line is crossing any structure).Control Valve location and arrangement.Continuation isometric drawing number (if the complete line do not fit in the single sheet).Dimensions of all components and spools.Slope (if it’s required as per project).Line elevations (it can be centerline or BOP (Bottom of Pipe) elevation).Angle allocation and direction ( clockwise or anti-clockwise).Points to be checked at drawing area are as follows. Design Pressure and Design Temperature (It’s not mandatory).Insulation and Heat Tracing Type (If the line is insulated only).Project Name, Project Code and Area Code.Here, you will learn to check the piping isometric drawing section-wise for ease of learning.
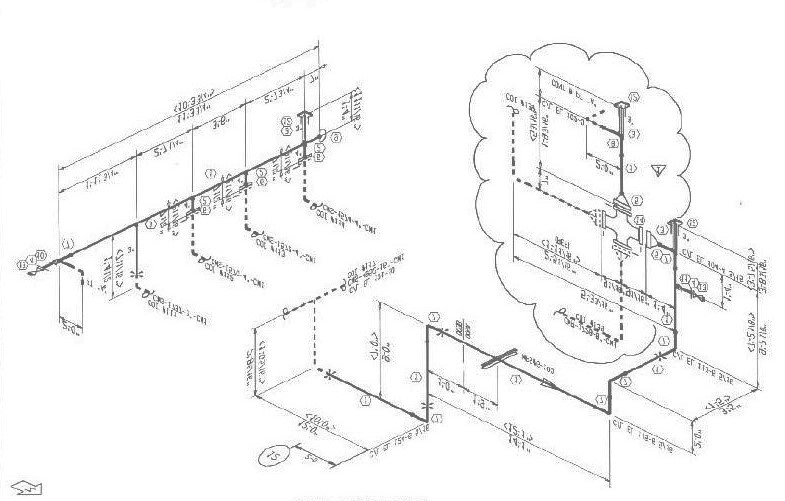
The isometric drawing sheet consists of four major parts viz title block, drawing area, BOQ (Bill of Quantity ) section, and Special requirement notes section. To check the connection/end requirements for mounting the instruments. To check special items type and their dimensions To check elevation and orientation of connected nozzle
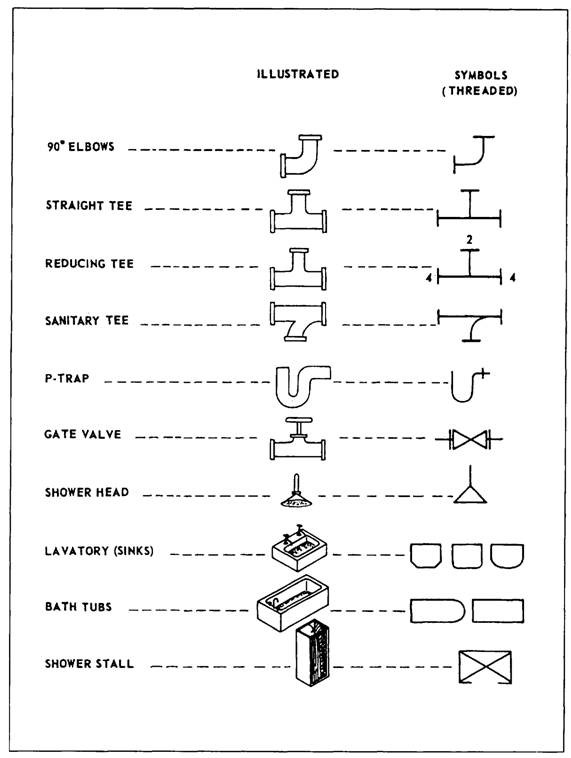
To check line route, dimension, elevation, valve orientation and co-ordinates To check Design Pressure & Temperature, stress critical lines, Hydro test pressure, inspection class and type, etc. To cross-check line number, line size, insulation, special requirement notes (like no pocket, press head), etc. P&ID (Piping and Instrumentation Diagram) Documents Required for Checking Piping Isometric Drawing Documents


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
